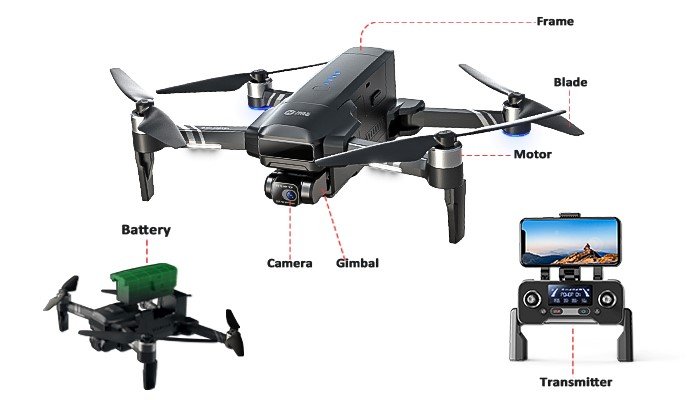
Understanding Components of Drone: Parts of Drone
Drones, also known as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), have emerged as integral tools across various industries, offering capabilities ranging from aerial photography to agriculture and package delivery. These technological wonders consist of numerous components meticulously engineered to work together seamlessly, enabling flight and functionality. Let’s explore the anatomy of drones and delve into what comprises these remarkable flying machines.
Components of Drone:
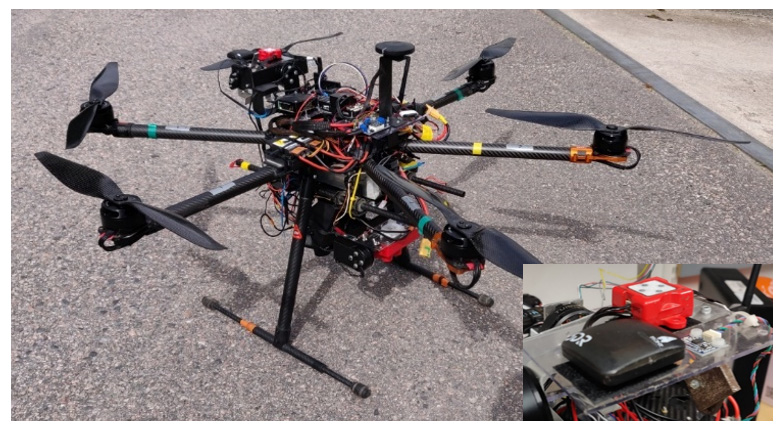
Frame: The Foundation of a Drone
The frame of a drone serves as its skeleton, providing structural support and housing all other components of Drone. Frames come in diverse shapes and materials, influencing factors such as stability, agility, and payload capacity. From lightweight carbon fiber frames designed for racing drones to durable plastic frames for consumer models, the choice of frame significantly impacts the drone’s performance.

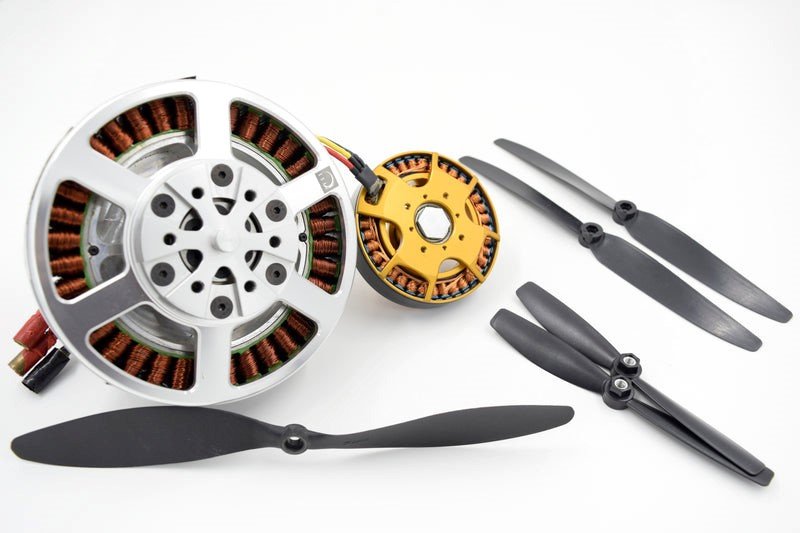
Motors and Propellers: Powerhouse of Flight
Motors and propellers are the driving force behind a drone’s flight. Typically arranged in a quadcopter configuration, these components generate thrust and lift. Brushless motors are favored for their efficiency and durability, while propeller size and pitch play crucial roles in determining flight characteristics such as speed and maneuverability.

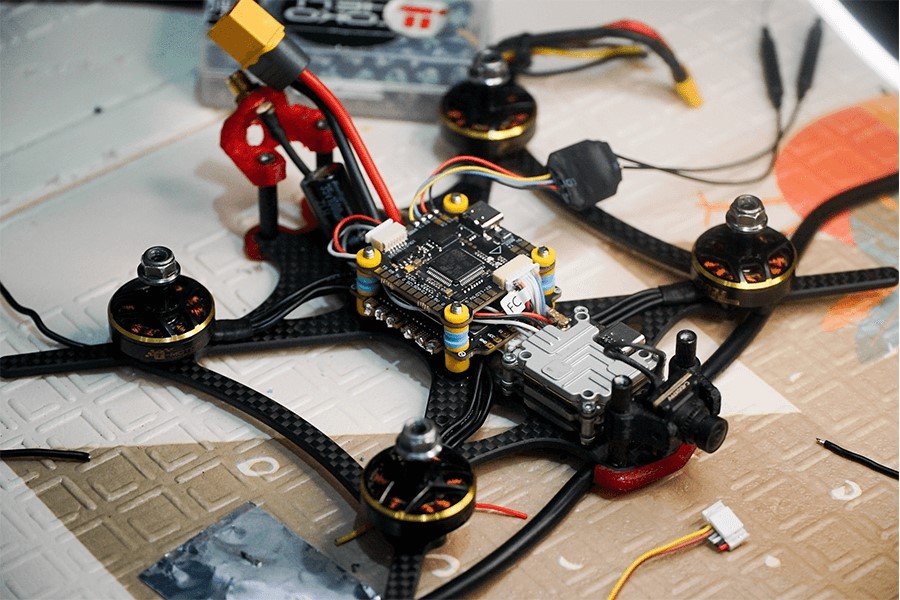
Flight Controller: The Drone’s Brain
The flight controller acts as the drone’s central processing unit, receiving data from various sensors and user inputs to stabilize and navigate the aircraft. It adjusts motor speeds and angles to maintain stability and execute flight commands. Advanced flight controllers offer features such as GPS navigation, altitude hold, and autonomous flight modes, enhancing the drone’s capabilities.

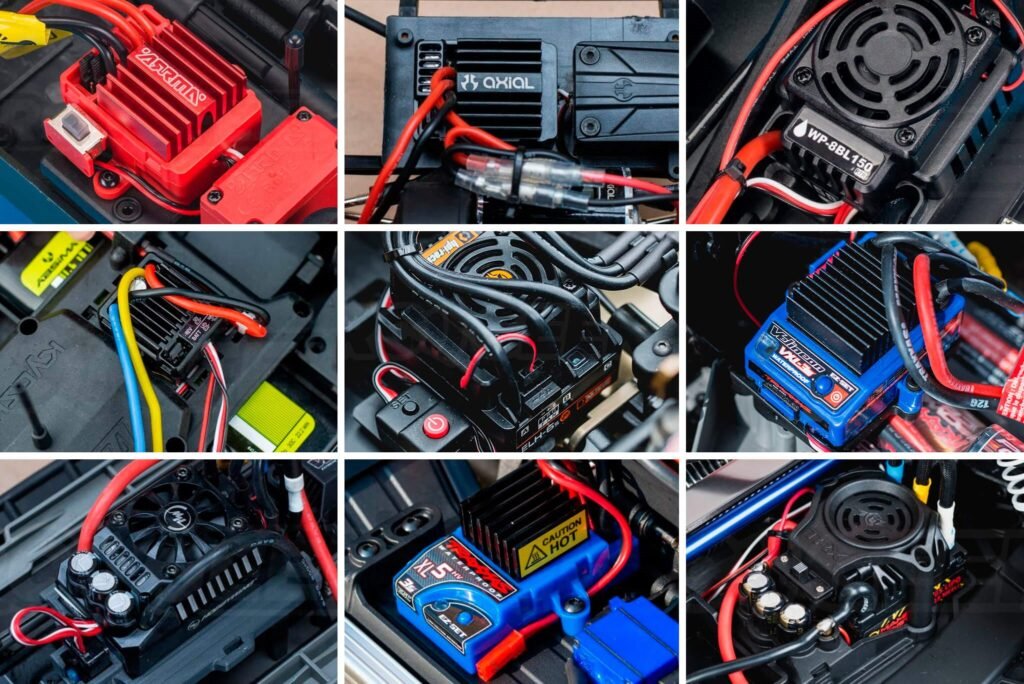
Electronic Speed Controllers (ESCs): Regulating Power
Electronic Speed Controllers (ESCs) regulate the power supplied to each motor based on commands from the flight controller. They convert signals from the flight controller into precise motor outputs, controlling the drone’s speed and direction. High-quality ESCs are essential for ensuring smooth and responsive flight performance.

Batteries: Providing Energy
Batteries are vital Components of Drone for powering the drone’s electronics and motors. Lithium polymer (LiPo) batteries are commonly used due to their high energy density and power-to-weight ratio. The capacity and voltage of the battery determine the drone’s flight time and overall performance, with larger batteries offering extended flight durations at the expense of added weight.

Propulsion System: Balancing Components
The propulsion system encompasses motors, propellers, and ESCs, working together to generate thrust and lift. Balancing these components is critical to achieving optimal performance and efficiency. Factors such as motor Kv rating, propeller size, and ESC capabilities must be carefully matched to ensure the desired flight characteristics.
Sensors: Gathering Data for Navigation
Drones rely on various sensors to gather data about their surroundings and orientation. Accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometers provide information about the drone’s motion and attitude, allowing the flight controller to maintain stability. GPS receivers enable accurate positioning and navigation, while additional sensors like barometers measure altitude.
Camera and Gimbal (for Camera Drones): Capturing Aerial Imagery
Camera drones are equipped with high-resolution cameras and gimbals for capturing aerial imagery and video. Gimbals stabilize the camera to counteract the drone’s movements, ensuring smooth and steady footage. Advanced camera drones may feature gimbal stabilization systems with multiple axes of movement for precise control.
Transmitter and Receiver: Wireless Communication
The transmitter, or remote controller, allows the pilot to communicate with the drone wirelessly. It sends control signals to the drone’s receiver, which interprets the commands and relays them to the flight controller. Modern transmitters feature ergonomic designs, multiple channels, and telemetry data feedback for enhanced control and situational awareness.
Payload (Optional): Carrying Additional Equipment
Drones can carry various payloads depending on their intended applications. This may include sensors for aerial mapping, thermal imaging cameras for search and rescue missions, or cargo for delivery purposes. Payload capacity and integration capabilities vary depending on the drone’s design and specifications.
Understanding Components of Drone: Insights and Customization
Understanding the components of a drone provides valuable insights into how these remarkable machines operate. It also opens up possibilities for customization and optimization, whether you’re a hobbyist building your own drone or a professional utilizing drones for commercial purposes. By carefully selecting and configuring components, you can tailor your drone to suit specific needs and achieve optimal performance.
The Future of Drones: Advancements and Applications
As technology continues to advance, drones will undoubtedly become even more versatile and capable. They will continue to reshape industries and push the boundaries of what’s possible in the skies. From improved battery technology to advanced sensors and autonomous capabilities, the future of drones holds immense potential for innovation and transformation across various sectors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, drones are complex yet fascinating machines comprised of various components working together harmoniously to achieve flight. From the frame to the propulsion system, each component plays a crucial role in ensuring the drone’s performance and functionality. By understanding these components, enthusiasts and professionals alike can unlock new possibilities for customization and optimization, paving the way for safe and successful flights in the future.
FAQs
- What are the essential components of a drone?
- The essential components include the frame, motors, propellers, flight controller, electronic speed controllers (ESCs), batteries, sensors, camera (for camera drones), transmitter, and receiver.
- How do drones navigate?
- Drones navigate using a combination of GPS, sensors, and onboard algorithms. GPS provides accurate positioning, while sensors gather data about the drone’s surroundings and orientation, enabling precise navigation.
- What is the flight time of a typical drone?
- The flight time of a drone depends on factors such as battery capacity, payload, and flying conditions. On average, consumer drones have flight times ranging from 15 to 30 minutes.
- Can drones be customized for specific purposes?
- Yes, drones can be customized for various purposes by selecting and configuring components according to specific needs. This customization allows for tailored solutions in industries such as agriculture, cinematography, and surveying.
- Are there regulations for flying drones?
- Yes, many countries have regulations governing the operation of drones, including restrictions on altitude, airspace, and registration requirements. It’s essential to familiarize yourself with local regulations before flying a drone.